|
Paper
Paper consists of fine vegetable
fibres which are extracted from wood. These fibres
are made of cellulose. Both coniferous (softwood
trees) and deciduous (hardwood trees) can be used
to provide the untreated material which is called
wood pulp. Cellulose fibres can also be taken
from other plants like hemp, flax, cotton and
bamboo. However the most common material source
to make paper from is wood. Wood pulp has numerous
different chemicals added to it. This is done
so the wood pulp can achieve the required texture
and surface finish required to make paper.
The stages involved in making paper
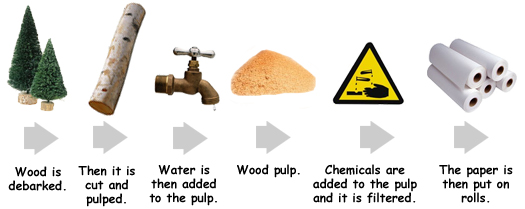
The paper making process
The paper making process has remained basically
the same for the last two thousand years. Tiny
chips of wood are cooked in water and chemicals
to make a mushy wood pulp. The pulp is then poured
through a filter or a fine mesh. As the water
drains away, the cellulose fibres (which are less
than 1mm in length) naturally join to form the
papers structure. The paper then moves through
a set of machine rollers which flattens the paper
and removes any left over water. Flattening the
paper makes the mesh of fibres stronger.
Paper comes in different sizes. ‘A’
sizes are the most common, standard sizes are
A4 and A3. Use the grid below to work out paper
sizes.
| Paper |
Size |
Note: |
| A6
|
105mm
x 148mm |
|
| A5 |
148mm
x 210mm |
(Twice
the size of A6) |
| A4 |
210mm
x 297mm |
(Twice
the size of A5) |
| A3 |
297mm
x 420mm |
(Twice
the size of A4) |
| A2 |
420mm
x 594mm |
(Twice
the size of A3) |
| A1
|
594mm
x 841mm |
(Twice
the size of A2) |
| A0 |
841mm
x 1189mm |
(Twice
the size of A1) |
Board
Board is a general term used to
describe a whole range of paper based material
such as cardboard, mounting board, corrugated
board, etc. Board is thicker, heavier and more
rigid than paper as it is made from several more
layers of pulp than paper is. Very thick board
is made by sticking sheets of paper or board together
in a process known as laminating.

Laminating paper-based board
with other materials creates boards with different
qualities. These are known as composite materials
e.g. – cereal packets, egg cartons, orange
juice cartons, etc. A good example is foil lined
board this has foil on one side of the board and
is used for fast food containers to keep moisture
an heat in. |








